PREPRINTS
2025
Mutational scanning reveals substrate-assisted autoregulation of the WNT destruction complex. Murugesh Padmanarayana, Saira Saklas, Parijat Sarkar, Mengxiao Ma, Ethan R. Garvin, Ethan Lee, Steven M Corsello, Sebastian Guettler, Ganesh V Pusapati, Rajat Rohatgi. bioRxiv 2025.10.17.683169; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.10.17.683169.
PDF | Pubmed
Design principles of a membrane-spanning ubiquitin ligase. Carys Williams, Laura M Nocka, George Hedger, Pragya Parashara, Els Pardon, Naomi R Latorraca, Ganesh V Pusapati, Dorothy Lartey, Lei Gao, Ljiljana Milenkovic, Rod Chalk, Jan Steyaert, Susan Marqusee, Loic Carrique, J Fernando Bazan, Sarah L Rouse, Jennifer H Kong, Christian Siebold, Rajat Rohatgi. bioRxiv 2025.09.11.675358; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.09.11.675358.
PDF | Pubmed
Plasma membrane accessible cholesterol is regulated by ACC1 and lipid droplets. Kalani M. Wijesinghe, Chai-wan Kim, Emily O. Schad, Shuo Li, Summer Chen, Erin Takeshima, Chandni B. Khandwala, Desiree Tillo, Andres M. Lebensohn, James A. Olzmann, Rajat Rohatgi, Maia Kinnebrew. bioRxiv 2025.08.21.671640; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.08.21.671640.
PDF | Pubmed
PUBLICATIONS
2026
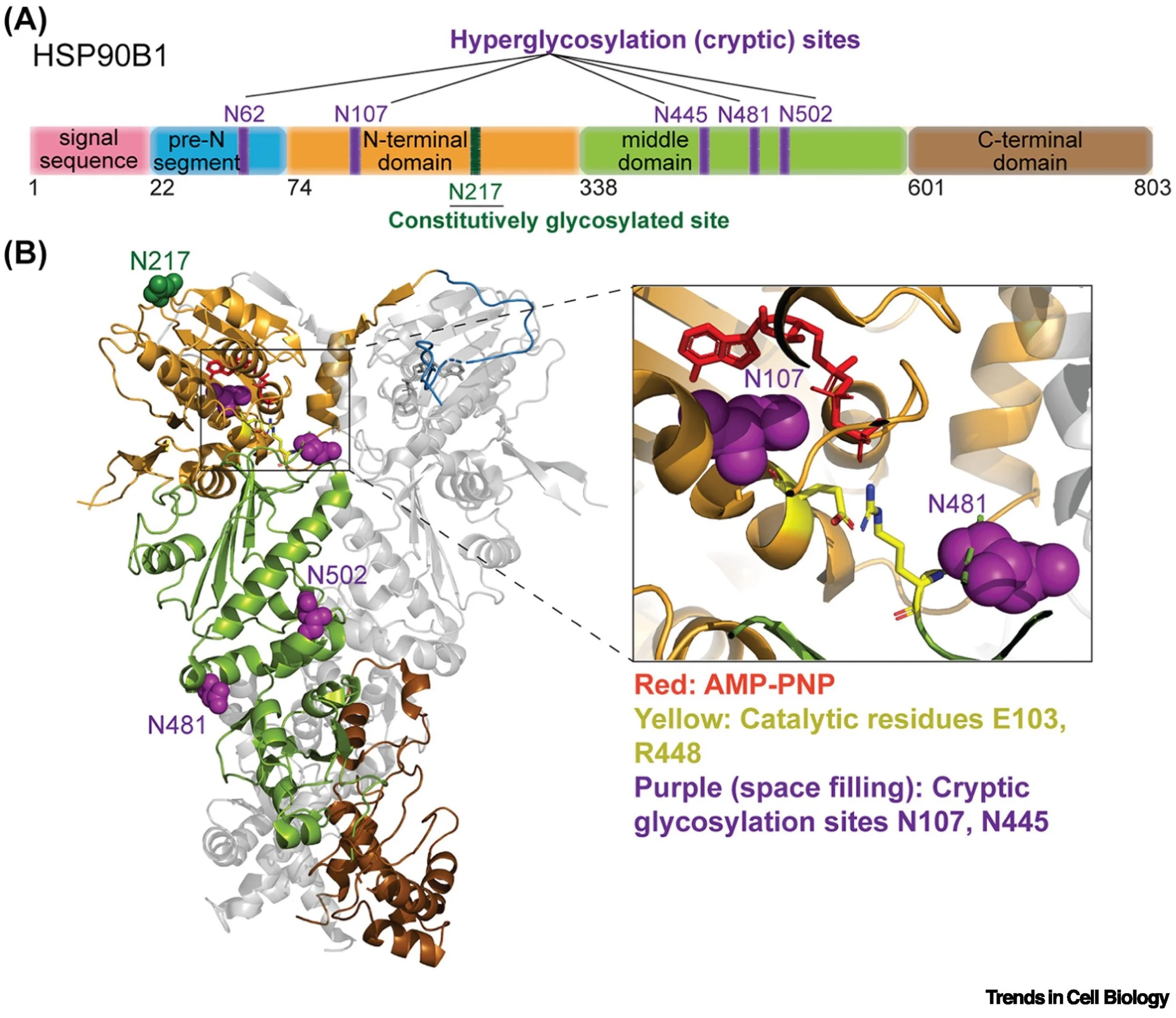
Expanding roles of N-glycosylation in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Ma M, Rohatgi R^. Trends in Cell Biology. (^corresponding author). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2025.12.001 Jan 14 2026.
2025
Structural basis of regulated N-glycosylation at the secretory translocon. Yamsek M*, Ma M *, Jha R *, Wan Y, Li Q, Zhong F, DeLong K, Ji Z, Rohatgi R^, Keenan R^. Nature. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09756-8 Nov 19 2025. PMID: 41261126
PDF | Pubmed
The TRIP12 E3 ligase induces SWI/SNF component BRG1-β-catenin interaction to promote Wnt signaling. Kassel S, Yuan K, Bunnag N, Neitzel LR, Lu W, Schwarzkopf A, Maines B, Loberg MA, Xu G, Adams A, McCray AD, Cho A, Rockouski M, Orton G, Goldsmith L, Aronno MMA, Spencer ZT, Khan OM, Ye F, Williams C, Lebensohn AM, Rohatgi R, Wang X, Weiss VL, Hong CC, Kettenbach AN, Robbins DJ, Ahmed Y^, Lee E^. Nature Communications (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-60535-5 doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60535-5. PMID: 40473626; PMCID: PMC12141612
Direct ionic stress sensing and mitigation by the transcription factor NFAT5 Khandwala CB*, Sarkar P*, Schmidt HB, Ma M, Pusapati GV, Lamoliatte F, Kinnebrew M, Patel BB, Tillo D, Lebensohn AM, Rohatgi R^. Science Advances. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author). https://www.science.org/doi/full/10.1126/sciadv.adu3194
cited by 3 [Google Scholar]
Serotonin signaling at cilia synapses. Review. DeLong K, Sheu SH. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 2025. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2025.102994. PMID: 40081222. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S095943882500025X?via%3Dihub
2024
Regulated N-glycosylation controls chaperone function and receptor trafficking. Ma M, Dubey R, Jen A, Pusapati GV, Singal B, Shishkova E, Overmyer KA, Cormier-Daire V, Fedry J, Aravind L, Coon JJ, Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author). Science 386,667-672(2024). DOI:10.1126/science.adp7201 https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adp7201
cited by 2 [Google Scholar]
The exocyst complex and intracellular vesicles mediate soluble protein trafficking to the primary cilium. Niedziółka SM, Datta S, Uśpieński T, Baran B, Skarżyńska W, Humke EW, Rohatgi R, Niewiadomski P^. ( ^corresponding author). Commun Biol. 7(1):213 (2024) PMID: 38378792
cited by 6 [Google Scholar]
A cholesterol-binding bacterial toxin provides a strategy for identifying a specific Scap inhibitor that blocks lipid synthesis in animal cells. Xu S, Smothers JC, Rye D, Endapally S, Chen H, Li S, Liang G, Kinnebrew M, Rohatgi R, Posner BA, Radhakrishnan A^. (^corresponding author) Proc Natl Acad Sci. 121(7):e2318024121 (2024) PMID: 38330014
cited by 7 [Google Scholar]
2023
The USP46 complex deubiquitylates LRP6 to promote Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Ng VH*, Spencer Z*, Neitzel LR, Nayak A, Loberg MA, Shen C, Kassel SN, Kroh HK, An Z, Anthony CC, Bryant JM, Lawson A, Goldsmith L, Benchabane H, Hansen AG, Li J, D'Souza S, Lebensohn AM, Rohatgi R, Weiss WA, Weiss VL, Williams C, Hong CC, Robbins DJ, Ahmed Y^, Lee E.^ (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author) Nat Commun. 14(1):6173. (2023) PMID: 37798301
cited by 14 [Google Scholar]
The USP46 deubiquitylase complex increases Wingless/Wnt signaling strength by stabilizing Arrow/LRP6. Spencer ZT*, Ng VH*, Benchabane H*, Siddiqui GS, Duwadi D, Maines B, Bryant JM, Schwarzkopf A, Yuan K, Kassel SN, Mishra A, Pimentel A, Lebensohn AM, Rohatgi R, Gerber SA, Robbins DJ, Lee E^, Ahmed Y^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author) Nat Commun. 14(1):6174. (2023) PMID: 37798281
cited by 5 [Google Scholar]
2022
Oxaliplatin disrupts nucleolar function through biophysical disintegration. Schmidt HB, Jaafar ZA, Wulff BE, Rodencal JJ, Hong K, Aziz-Zanjani MO, Jackson PK, Leonetti MD, Dixon SJ, Rohatgi R^, Brandman^ (^corresponding author) Cell Rep. 41(6):111629. (2022). PMID: 36351392
cited by 40 [Google Scholar]
Receptor control by membrane-tethered ubiquitin ligases in development and tissue homeostasis. Lebensohn AM^, Bazan JF^, Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author) Curr Top Dev Biol 150:25-89 (2022). PMID: 35817504
cited by 12 [Google Scholar]
Patched 1 regulates Smoothened by controlling sterol binding to its extracellular cysteine-rich domain. Kinnebrew M, Woolley RE, Ansell TB, Byrne EFX, Frigui S, Luchetti G, Sircar R, Nachtergaele S, Mydock-McGrane L, Krishnan K, Newstead S, Sansom MSP, Covey DF, Siebold C^, Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author) Science Advances 8(22):eabm5563 (2022). PMID: 35658032
cited by 31 [Google Scholar]
Measuring and Manipulating Membrane Cholesterol for the Study of Hedgehog Signaling. Kinnebrew M*, Johnson KA*, Radhakrishnan A^, Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author) Methods Mol Biol. 2374:73-87. (2022) PMID: 34562244
cited by 1 [Google Scholar]
2021
Hedgehog-Interacting Protein is a multimodal antagonist of Hedgehog signalling.
Griffiths SC*, Schwab RA*, El Omari K, Bishop B, Iverson EJ, Malinauskas T, Dubey R, Qian M, Covey DF, Gilbert RJC, Rohatgi R, Siebold C^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Nature Communications 12(1):7171. (2021). PMID: 34887403
cited by 28 [Google Scholar]
Patched 1 reduces the accessibility of cholesterol in the outer leaflet of membranes. Kinnebrew M, Luchetti G, Sircar R, Frigui S, Viti LV, Naito T, Beckert F, Saheki Y, Siebold C, Radhakrishnan A, Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author) eLife 10:e70504 (2021) PMID: 34698632
cited by 51 [Google Scholar]
Gene-teratogen interactions influence the penetrance of birth defects by altering Hedgehog signaling strength. Kong JH, Young CB, Pusapati GV, Espinoza FH, Patel CB, Beckert F, Ho S, Patel BP, Gabriel GC, Aravind L, Bazan JF, Gunn TM^, Lo CW^, and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author) Development 148 (19):dev199867 (2021). PMID: 34486668
cited by 9 [Google Scholar]
Human-chimpanzee fused cells reveal cis-regulatory divergence underlying skeletal evolution.
Gokhman D^, Agoglia RM, Kinnebrew M, Gordon W, Sun D, Bajpai VK, Naqvi S, Chen C, Chan A, Chen C, Petrov DA, Ahituv N, Zhang H, Mishina Y, Wysocka J, Rohatgi R, and Fraser HB^. (^corresponding author) Nature Genetics 53(4):467-476. (2021). PMID: 33731941
cited by 57 [Google Scholar]
Bile acid biosynthesis in Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome bypassing cholesterol: Potential importance of pathway intermediates.
Abdel-Khalik J, Hearn T, Dickson AL, Crick PJ, Yutuc E, Austin-Muttitt K, Bigger BW, Morris AA, Shackleton CH, Clayton PT, Iida T, Sircar R, Rohatgi R, Marschall HU, Sjövall J, Björkhem I, Mullins JGL, Griffiths WJ^, and Wang Y^. (^corresponding author) The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 206:105794.(2021). PMID: 33246156
cited by 20 [Google Scholar]
2020
Mutations in GRK2 cause Jeune syndrome by impairing Hedgehog and canonical Wnt signaling.
Bosakova M, Abraham SP, Nita A, Hruba E, Buchtova M, Taylor SP, Duran I, Martin J, Svozilova K, Barta T, Varecha M, Balek L, Kohoutek J, Radaszkiewicz T, Pusapati GV, Bryja V, Rush ET, Thiffault I, Nickerson DA, Bamshad MJ; University of Washington Center for Mendelian Genomics, Rohatgi R, Cohn DH, Krakow D^, and Krejci P^. (^corresponding author)
EMBO Molecular Medicine 12(11):e11739 (2020). PMID: 33200460
cited by 24 [Google Scholar]
Cholesterol access in cellular membranes controls Hedgehog signaling.
Radhakrishnan A*^, Rohatgi R*^, and Siebold C*^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Nature Chemical Biology 16(12):1303-1313 (2020). PMID: 33199907
cited by 127 [Google Scholar]
A Membrane-Tethered Ubiquitination Pathway Regulates Hedgehog Signaling and Heart Development.
Kong JH*, Young CB*, Pusapati GV*, Patel CB, Ho S, Krishnan A, Lin JI, Devine W, Moreau de Bellaing A, Athni TS, Aravind L, Gunn TM^, Lo CW^, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Developmental Cell 55(4):432-449 (2020). PMID: 32966817
cited by 31 [Google Scholar]
Flow Homogenization Enables a Massively Parallel Fluidic Design for High-throughput and Multiplexed Cell Isolation.
Ooi C^, Earhart CM, Hughes CE, Lee JR, Wong DJ, Wilson RJ, Rohatgi R, and Wang SX^. (^corresponding author)
Advanced Materials Technologies 5(5):1900960 (2020). PMID: 33072854
cited by 1 [Google Scholar]
R-spondins engage heparin sulfate proteoglycans to potentiate WNT signaling.
Dubey R*, Kerkhof PV, Jordens I, Malinauskas T, Pusapati GV, McKenna JK, Li D, Carette JE, Ho M, Siebold C, Maurice M, Lebensohn AM*^, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
eLife 9:e54469 (2020). PMID: 32432544
cited by 54 [Google Scholar]
High-throughput Flow Cytometry Assay to Investigate TDP43 Splicing Function.
Schmidt HB^ and Rohatgi R. (^corresponding author)
Bio-protocol 10(8):e3594. (2020). PMID: 33659560
cited by 4
TDP-43 α-helical structure tunes liquid–liquid phase separation and function.
Conicella A*E, Dignon GL*, Zerze GH, Schmidt HB, Alexandra MD, Kim YC, Rohatgi R, Ayala YM, Mittal J^, and Fawzi NL^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Proceedings of the National Academy. 117(11):5883-2894. (2020). PMID: 32132204
cited by 339 [Google Scholar]
Lipid droplets can promote drug accumulation and activation.
Dubey R, Stivala CE, Nguyen HQ, Goo YH, Paul A, Carette JE, Trost BM, and Rohatgi R^.(^corresponding author)
Nature Chemical Biology 16(2):206-213 (2020) PMID: 31932720
cited by 59 [Google Scholar]
2019
Cholesterol accessibility at the ciliary membrane controls hedgehog signaling.
Kinnebrew M*, Iverson EJ*, Patel BB, Pusapati GV, Kong JH, Johnson KA, Luchetti G, Eckert KM, McDonald JG, Covey DF, Siebold C, Radhakrishnan A^, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
eLife 8:e50051 (2019). PMID: 31657721
PDF|PubMED
cited by 131 [Google Scholar]
Phase separation-deficient TDP43 remains functional in splicing.
Schmidt HB^, Barreau A, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Nature Communications 10(1):4890 (2019). PMID: 31653829
cited by 154 [Google Scholar]
The morphogen Sonic Hedgehog inhibits its receptor Patched by a pincer grasp mechanism.
Rudolf AF*, Kinnebrew M*, Kowatsch C*, Ansell TB*, El Omari K*, Bishop B, Pardon E, Shwab RA, Malinauskas T, Qian M, Duman R, Covey DF, Steyaert J, Wagner A, Sansom MSP, Rohatgi R^, and Siebold C^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Nature Chemical Biology 15(10):975-982. (2019). PMID: 31548691.
cited by 74 [Google Scholar]
Structures of vertebrate Patched and Smoothened reveal intimate links between cholesterol and Hedgehog signalling.
Kowatsch C*, Woolley RE*, Kinnebrew M, Rohatgi R^, and Siebold C^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Current Opinion in Structural Biology 57:204-214. (2019). PMID: 31247512
cited by 63 [Google Scholar]
Biochemical mechanisms of vertebrate Hedgehog signaling.
Kong JH, Siebold C^, and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
Development 146(10):dev166892 (2019). PMID: 31092502.
PDF|PubMED
cited by 255 [Google Scholar]
Discovery of gene regulatory elements through a new bioinformatics analysis of haploid genetic screens.
Patel BB*, Lebensohn AM*^, Pusapati GV, Carette JE, Salzman J^, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
PLoS One 14(1):e0198463 (2019). PMID: 30695034
PDF|PubMED
Cholesterol interaction sites on the transmembrane domain of the Hedgehog signal transducer and class F G protein-coupled receptor Smoothened.
Hedger G, Koldsø H, Chavent M, Siebold C, Rohatgi R, and Sansom MSP^. (^corresponding author)
Structure 27(3):549-559.e2 (2019). PMID: 30595453
cited by 90 [Google Scholar]
2018
Spatiotemporal manipulation of ciliary glutamylation reveals its roles in intraciliary trafficking and Hedgehog signaling.
Hong SR, Wang CL, Huang YS, Chang YC, Pusapati GV, Lin CY, Hsu N, Cheng HC, Chiang YC, Huang WE, Shaner NC, Rohatgi R, Inoue T^, and Lin YC^. (^corresponding author)
Nature Communications. 9(1):1732 (2018). PMID: 29712905
cited by 73 [Google Scholar]
A single N-terminal phosphomimic disrupts TDP-43 polymerization, phase separation, and RNA splicing.
Wang A*, Conicella AE*, Schmidt HB, Martin EW, Rhoads SN, Reeb AN, Nourse A, Ramirez Montero D, Ryan VH, Rohatgi R, Shewmaker F, Naik MT, Mittag T, Ayala YM, and Fawzi NL^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
The EMBO Journal. pii: e97452 (2018). PMID: 29438978.
cited by 417 [Google Scholar]
G-protein coupled receptors control the sensitivity of cells to the morphogen Sonic Hedgehog.
Pusapati GV*, Kong JH*, Patel BB, Gouti M, Sagner A, Sircar R, Luchetti G, Ingham PW, Briscoe J, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Science Signaling. 11(516):eaa05749 (2018). PMID: 29438014.
cited by 71 [Google Scholar]
R-spondins can potentiate WNT signaling without LGRs.
Lebensohn AM^ and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
eLife. pii: e33126 (2018). PMID: 29405118.
cited by 149 [Google Scholar]
CRISPR screens uncover genes that regulate target cell sensitivity to the morphogen Sonic Hedgehog.
Pusapati GV*^, Kong JH*, Patel BB*, Krishnan A, Sagner A, Kinnebrew M, Briscoe J, Aravind L, and Rohatgi^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Developmental Cell. 44(1):113-129 (2018). PMID: 29290584.
cited by 150 [Google Scholar]
2017
Multiple ligand binding sites regulate the Hedgehog signal transducer Smoothened in vertebrates.
Byrne EF, Luchetti G, Rohatgi R^, and Siebold C^. (^corresponding author)
Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 51:81-88 (2017). PMID: 29268141.
cited by 72 [Google Scholar]
Dynamic Remodeling of Membrane Composition Drives Cell Cycle through Primary Cilia Excision.
Phua SC^, Chiba S, Suzuki M, Su E, Roberson EC, Pusapati GV, Setou M, Rohatgi R, Reiter JF, Ikegami K^, and Inoue T^. (^corresponding author)
Cell. 168(1-2):264-279 (2017). PMID: 28086093.
cited by 348 [Google Scholar]
2016
Comparative genetic screens in human cells reveal new regulatory mechanisms in WNT signaling.
Lebensohn AM, Dubey R, Neitzel LR, Tacchelly-Benites O, Yang E, Marceau CD, Davis EM, Patel BB, Bahrami-Nejad Z, Travaglini KJ, Ahmed Y, Lee E, Carette JE^, and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
eLife. 5: e21459 (2016). PMID: 27996937.
cited by 59 [Google Scholar]
Cholesterol activates the G-protein coupled receptor Smoothened to promote Hedgehog signaling.
Luchetti G*, Sircar R*, Kong JH, Nachtergaele S, Sagner A, Byrne EF, Covey DF, Siebold C^, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
eLife. pii: e20304 (2016). PMID: 27705744.
cited by 257 [Google Scholar]
Chromatin-Remodeling Complex SWI/SNF Controls Multidrug Resistance by Transcriptionally Regulating the Drug Efflux Pump ABCB1.
Dubey R*, Lebensohn AM*, Bahrami-Nejad Z, Marceau C, Champion M, Gevaert O, Sikic BI, Carette JE^, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Cancer Research. 76(19):5810-5821 (2016). PMID: 27503929.
cited by 45 [Google Scholar]
In vivo formation of vacuolated multi-phase compartments lacking membranes.
Schmidt HB^ and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
Cell Reports. 16(5):1228-1236 (2016). PMID: 27452472.
cited by 183 [Google Scholar]
Structural basis of Smoothened regulation by its extracellular domains.
Byrne EFX*, Sircar R*, Miller PS, Hedger G, Luchetti G, Nachtergaele S, Tully MD, Mydock-McGrane L, Covey DF, Rambo RP, Sansom MSP, Newstead S*, Rohatgi R^, and Siebold C^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Nature. 535(7613):517-522 (2016). PMID: 27437577.
cited by 381 [Google Scholar]
An essential role for Grk2 in Hedgehog signaling downstream of Smoothened.
Zhao Z*, Lee RT*, Pusapati GV, Iyu A, Rohatgi R, and Ingham PW^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
EMBO Reports. 17(5):739-52 (2016). PMID: 27113758.
cited by 52 [Google Scholar]
2015
Functional Divergence in the Role of N-Linked Glycosylation in Smoothened Signaling.
Marada S, Navarro G, Truong A, Stewart DP, Arensdorf AM, Nachtergaele S, Angelats E, Opferman JT, Rohatgi R, McCormick PJ, and Ogden SK^. (^corresponding author)
PLoS Genetics. 11(8):e1005473 (2015). PMID: 26291458.
cited by 50 [Google Scholar]
Notch activity modulates the responsiveness of neural progenitors to Sonic Hedgehog signaling.
Kong JH*, Yang L*, Dessaud E, Chuang K, Moore DM, Rohatgi R, Briscoe J, and Novitch BG^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Developmental Cell. 33(4): 373-387 (2015). PMID: 25936505.
cited by 149 [Google Scholar]
Rapid Screening of Gli2/3 Mutants Using the Flp-In System.
Niewiadomski P^ and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
Methods in Molecular Biology. 1322:125-30 (2015). PMID: 26179044.
PDF |PubMED
cited by 2 [Google Scholar]
Measuring Gli2 Phosphorylation by Selected Reaction Monitoring Mass Spectrometry.
Ahrends R*, Niewiadomski P*, Teruel MN, Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Methods in Molecular Biology. 1322:105-123 (2015). PMID: 26179041.
PDF |PubMED
Measuring Expression Levels of Endogenous Gli Genes by Immunoblotting and Real-Time PCR.
Niewiadomski P and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
Methods in Molecular Biology. 1322:91-92 (2015). PMID: 26179041.
cited by 11 [Google Scholar]
2014
Location, location, and location: compartmentalization of Hedgehog signaling at primary cilia.
Pusapati GV^ and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
The EMBO Journal. 33(17):1852-4 (2014). PMID: 25037564.
cited by 13 [Google Scholar]
Frontiers in hedgehog signal transduction.
Guerrero I^ and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology. 33:50-1 (2014). PMID: 24946961.
PDF |PubMED
cited by 1 [Google Scholar]
A novel osteogenic oxysterol compound for therapeutic development to promote bone growth: activation hedgehog signaling and osteogenesis through smoothened binding.
Montgomery SR, Nargizyan T, Meliton V, Nachtergaele S, Rohatgi R, Stappenbeck F, Jung ME, Johnson JS, Aghdasi B, Tian H, Weintraub G, Inoue H, Atti E, Tetradis S, Pereira RC, Hokugo A, Alobaidaan R, Tan Y, Hahn TJ, Wang JC, and Parhami F.
Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 29(8):1872-85 (2014). PMID: 24591126.
cited by 82 [Google Scholar]
G-protein-coupled receptors, Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia. Seminars in Cell and Developmental Biology.
Mukhopadhyay S^ and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology. (2014). PMID: 24845016.
cited by 160 [Google Scholar]
Tracking the subcellular fate of 20(S)-hydroxycholesterol with click chemistry reveals a transport pathway to the Golgi.
Peyrot SM*, Nachtergaele S*, Luchetti G, Mydock-McGrane LK, Fujiwara H, Scherrer D, Jallouk A, Schlesinger PH, Ory DS, Covey DF, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 289(16):11095-11110 (2014). PMID: 24596093.
cited by 28 [Google Scholar]
EFCAB7 and IQCE regulate Hedgehog signaling by tethering the EVC-EVC2 complex to the base of primary cilia.
Pusapati GV*, Hughes CE*, Dorn KV*, Zhang D, Sugianto P, Aravind L^, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Developmental Cell. 28(5):483-496 (2014). PMID: 24582806.
cited by 102 [Google Scholar]
Gli protein activity is controlled by multi-site phosphorylation in vertebrate Hedgehog signaling.
Niewiadomski P^, Kong JH, Ahrends R, Ma Y, Humke EW, Khan S, Teruel MN, Novitch BG, and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
Cell Reports. 6(1):168-81 (2014). PMID: 24373970.
cited by 283 [Google Scholar]
2013
Structure and function of the Smoothened extracellular domain in vertebrate Hedgehog signaling.
Nachtergaele S*, Whalen DM*, Mydock LK, Zhao Z, Malinauskas T, Krishnan K, Ingham PW, Covey DF, Siebold C^, and Rohatgi R^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
eLife. 2:e01340 (2013). PMID: 24171105.
cited by 191 [Google Scholar]
Chemically inducible diffusion trap at cilia reveals molecular sieve-like barrier.
Lin YC, Niewiadomski P*, Lin B*, Nakamura H*, Phua SC, Jiao J, Levchenko A, Inoue T, Rohatgi R, and Inoue T^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Nature Chemical Biology. 9(7):437-443 (2013). PMID: 23666116.
cited by 150 [Google Scholar]
Isolation and mutational analysis of circulating tumor cells from lung cancer patients with magnetic sifters and biochips.
Earhart CM, Hughes CE, Gaster RS, Ooi CC, Wilson RJ, Zhou LY, Humke EW, Xu L, Wong DJ, Willingham SB, Schwartz EJ, Weissman IL, Jeffrey SS, Neal JW, Rohatgi R, Wakelee HA, and Wang SX^. (^corresponding author)
Lab on a Chip. 14(1), 78-88 (2013). PMID: 23969419.
cited by 207 [Google Scholar]
Cancer risk after use of recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2 for spinal arthrodesis.
Carragee EJ, Chu G, Rohatgi R, Hurwitz EL, Weiner BK, Yoon ST, Comer G, and Kopjar B.
Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 95(17), 1537-45 (2013). PMID: 24005193.
cited by 301 [Google Scholar]
2012
Oxysterols are allosteric activators of the oncoprotein Smoothened.
Nachtergaele S, Mydock LK, Krishnan K, Rammohan J, Schlesinger PH, Covey DF^, and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
Nature Chemical Biology. 8(2):211-20 (2012). PMID: 22231273.
cited by 332 [Google Scholar]
A Smoothened-Evc2 complex transduces the Hedgehog signal at primary cilia.
Dorn K, Hughes CE and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
Developmental Cell. 23(4):823-35 (2012). PMID: 22981989.
cited by 201 [Google Scholar]
Singapore signalling: the 2012 hedgehog pathway cocktail.
Briscoe J^ and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
EMBO Reports. 13(7):580-3 (2012). PMID: 22688966.
cited by 1 [Google Scholar]
2010
The output of Hedgehog signaling is controlled by the dynamic association between Suppressor of Fused and the Gli proteins.
Humke EW, Dorn KV, Milenkovic L, Scott MP, and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
Genes & Development. 24(7):670-82 (2010). PMID: 20360384.
cited by 539 [Google Scholar]
Role of lipid metabolism in smoothened derepression in hedgehog signaling.
Yavari A*, Nagaraj R*, Owusu-Ansah E, Folick A, Ngo K, Hillman T, Call G, Rohatgi R, Scott MP, and Banerjee U^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Developmental Cell. 19(1):54-65 (2010). PMID: 20643350
cited by 123 [Google Scholar]
The ciliary membrane.
Rohatgi R^ and Snell WJ^. (^corresponding author)
Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 22(4):541-6 (2010). PMID: 20399632.
cited by 233 [Google Scholar]
2009
Hedgehog signal transduction by smoothened: pharmacological evidence for a two-step activation process.
Rohatgi R*, Milenkovic L*, Corcoran RB, and Scott MP^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA. 106(9):3196-201 (2009). PMID: 19218434.
cited by 357 [Google Scholar]
Lateral transport of Smoothened from the plasma membrane to the membrane of the cilium.
Milenkovic L, Scott MP^, and Rohatgi R^. (^corresponding author)
The Journal of Cell Biology. 2009; 187 (3): 365-74
cited by 321 [Google Scholar]
2007
Patched1 regulates Hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium.
Rohatgi R*, Milenkovic L*, and Scott MP^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Science. 2007; 317 (5836): 372-376
cited by 1692 [Google Scholar]
Patching the gaps in Hedgehog signaling.
Rohatgi R and Scott MP^. (^corresponding author)
Nature Cell Biology. 2007; 9 (9): 1005-1009
cited by 264 [Google Scholar]
2004
Loss-of-function Analysis of EphA Receptors in Retinotectal mapping.
Feldheim DA, Nakamoto M, Osterfield M, Gale NW, DeChiara TM, Rohatgi R, Yancopoulos GD, Flanagan JG^. (^corresponding author)
The Journal of Neuroscience. 2004; 24 (10): 2542-2550
cited by 178 [Google Scholar]
Toca-1 Mediates Cdc42- Dependent Actin Nucleation by Activating the N-WASP-WIP Complex.
Ho HY*, Rohatgi R*, Lebensohn A, Ma L, Li L, Gygi SP, and Kirschner MW*. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Cell. 2004; 118 (2): 203-216
cited by 532 [Google Scholar]
2001
CR16 Forms a Complex with N-WASP in Brain and is a Novel Member of a Conserved Proline-Rich Actin-Binding Protein Family.
Ho HY*, Rohatgi R*, Ma L, and Kirschner MW^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA. 2001; 98 (20): 11306-11311
cited by 138 [Google Scholar]
Nck and Phosphatidylinositol 4,5 Bisphosphate Synergistically Activate Actin Polymerization Through the N-WASP-Arp2/3 Pathway.
Rohatgi R, Nollau P, Ho HY, Kirschner MW^, and Mayer BJ. (^corresponding author)
The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001; 276 (28): 26448-26452
cited by 524 [Google Scholar]
WIP Regulates N-WASP-Mediated Actin Polymerization and Filopodium Formation.
Martinez-Quiles N, Rohatgi R, Anton IM, Medina M, Saville SP, Miki H, Yamaguchi H, Takenawa T, Hartwig JH, Geha RS^, and Ramesh N. (^corresponding author)
Nature Cell Biology. 2001; 3 (5): 484-491
cited by 360 [Google Scholar]
1999
The Interaction Between N-WASP and the Arp2/3 Complex Links Cdc42-Dependent Signals to Actin Assembly.
Rohatgi R*, Ma L*, Miki H, Lopez M, Kirchhausen T, Takenawa T, and Kirschner MW^. (*equal contribution; ^corresponding author)
Cell. 1999; 97 (2): 221-231
cited by 1756 [Google Scholar]
1996
Non-Enzymatic, Template-Directed Ligation of Oligoribonucleotides is Highly Regioselective for the Formation of 3'-5'-Phosphodiester Bonds.
Rohatgi R, Bartel DP, Szostak JW. (^corresponding author)
Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1996; 118(14):3340-3344
cited by 153 [Google Scholar]
Kinetic and Mechanistic Analysis of Non-Enzymatic, Template-Directed Oligoribonucleotide Ligation.
Rohatgi R, Bartel DP, Szostak JW. (^corresponding author)
Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1996; 118(14):3332-3339
cited by 152 [Google Scholar]
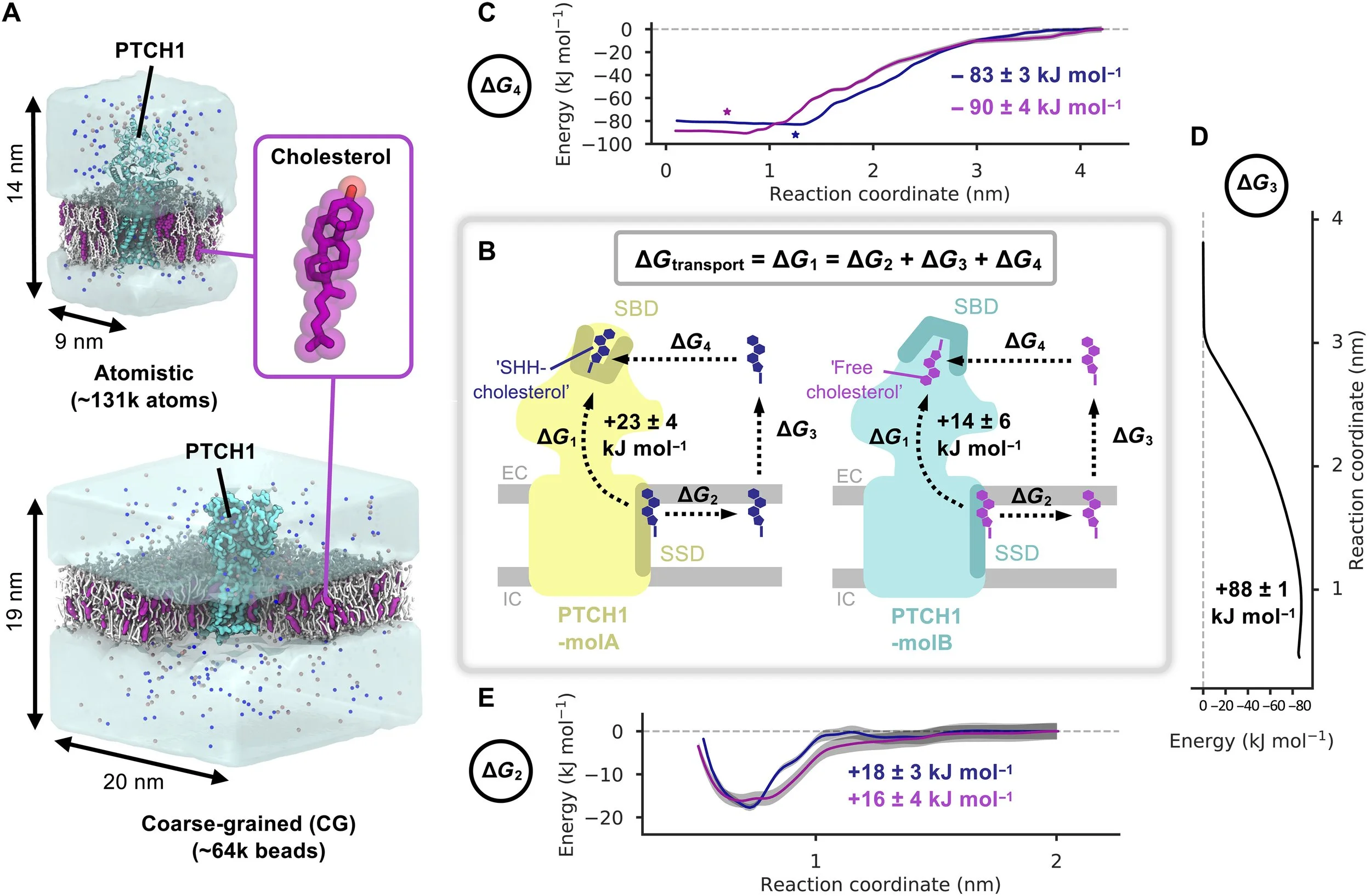
Ansell et al. Sci Adv 2023 Fig. 1